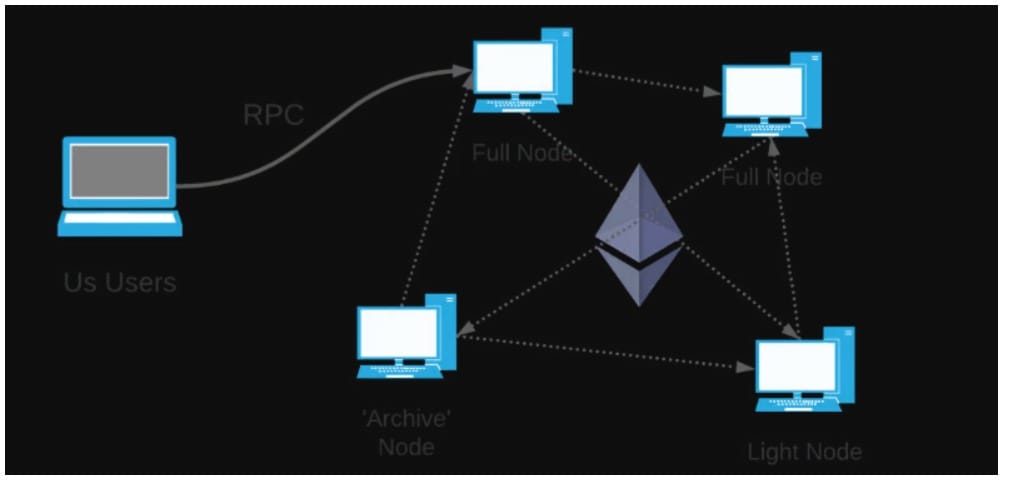
Decentralized applications (dApps), such as crypto wallets, need to interact with the blockchain to execute actions like sending transactions and checking block details. To enable this, dApps use a Remote Procedure Call (RPC) to connect with the network using nodes.
In crypto, a node is a computer that links an asset to the decentralized network. It helps support the system by checking and sharing transactions. In addition, a node compiles the full details of the decentralized server. For more context, any computer connected to a blockchain is considered a node. Several types of nodes exist today. Plus, each node is assigned a distinct task to execute within the network. In this article, these concepts will be explored.
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Table of Contents
What is a Remote Procedure Call (RPC)?
A Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is a mechanism that enables an application to interact with other systems and services. It lets one program (the client) ask another program (the server), often located on another computer or network, to perform a task. Moreover, it accomplishes this without requiring knowledge of the server’s technical details.
For instance, you can use RPC from your personal computer to request information or services from a remote server. When the client sends a request, the server carries out a specific task or function, known as a subroutine.
In a decentralized setup, software needs to interact with network data to ensure efficient execution. In this setup, the app acts as the client, and the server it talks to is known as an RPC node.
What is an RPC Node?
An RPC node is a computer that enables apps to communicate with a blockchain by responding to Remote Procedure Call (RPC) requests. For example, a Monero node might run the monerod daemon to access and process blockchain data while supporting wallet connections and network syncing.
Monero has different kinds of nodes, including full nodes and remote nodes. Each node has different privacy, storage, and syncing capabilities. On the other hand, Solana offers two main types of nodes: validator nodes and RPC nodes. Validator nodes take part in the network’s consensus process and earn rewards for verifying blocks, while RPC nodes mainly provide data and services to apps built on Solana.
Key Notes:
- Client-Server Model: In this setup, RPC (Remote Procedure Call) nodes function as servers, handling requests from clients by processing them and returning the necessary data.
- Simplified Interaction: This model facilitates easy connection between users and developers, and blockchain networks. They don’t need to understand the complex inner workings of the system to build or use blockchain-based applications.
- Accessibility: Instead of running and managing their own blockchain nodes, developers can use RPC nodes offered by external infrastructure providers. This gives them reliable access to blockchain networks with less hassle and technical overhead.
What is an RPC Endpoint?
RPC endpoints are basically the address your app uses to talk to a server and request data. For example, when you connect your app to an Ethereum RPC endpoint, you can easily access up-to-date blockchain information and perform actions like reading balances or sending transactions.
A computer (called a node) that runs the right software can handle these RPC requests. When an RPC endpoint is running on a node, it means the software is using that service to access decentralized network data. So, an RPC node is just a node that offers an RPC endpoint, and the terms RPC node and RPC endpoint usually mean the same thing.

Types of RPC Endpoints Explained
Node RPC endpoints fall into two broad categories. The other RPC endpoints supplement these two by enabling apps to maintain fault-tolerant copies of their RPC endpoints.
1. Public RPC Endpoint
Public RPC endpoints are open access points that anyone can use to interact with a blockchain; for example, to read data or send transactions. These endpoints are free and available at any time because they’re shared resources provided by the blockchain itself.
However, because they are public and used by many people, they often have limits on how many requests you can send (rate-limited). They are not designed for large-scale apps, and you won’t get customer support or strong performance guarantees if something goes wrong.
2. Private RPC Endpoint
Private RPC endpoints are dedicated to serving just an app, giving faster and more reliable access to the blockchain without interference from other users. These endpoints are usually provided by services that run custom blockchain nodes. They often come with service agreements (SLAs) that guarantee high performance and uptime.
3. Alternative RPC Endpoint
Alternative RPC endpoints are backup connections you can use if your main one goes down. They help your app keep running smoothly even if there’s an issue with the primary endpoint. If you rely on only one RPC endpoint and it fails, your app and user transactions could stop working. Using alternative endpoints helps avoid this by making sure your app always has a way to connect to the blockchain.
How RPC Nodes Function in a Blockchain Network
RPC nodes provide programs with access to blockchain information. A program requests an RPC node for data whenever it needs data from the blockchain. The node recognizes the requested data in the blockchain and returns it to the program. The technology involved in how such blockchain requests work is expanded on below:
The JSON-RPC Protocol
Most blockchains use a protocol called JSON-RPC to handle requests. It’s light and efficient, and it’s what allows apps to talk to the blockchain through RPC nodes. For better clarity, your app is the client, the RPC node is the server, and JSON-RPC is the protocol they use for communication.
Each blockchain presents a list of its own JSON-RPC methods which an app uses to request different types of data. Some, such as Ethereum, support the typical list of methods for retrieving data from the network. These methods are usually divided into three types: gossip, state, and history methods. The gossip methods help to stay in sync with the chain’s new block. Meanwhile, the state methods tell the current status of the data on the network. Lastly, the history methods fetch previous data or blocks.
Whenever an application requires data from the blockchain, it calls for it by sending a request in the form of JSON-RPC methods to the RPC node. In turn, the protocol replies with the information.
Practical Applications of RPC in Blockchain Development
- Wallet and Account Management: RPC offers wallet and account management support. Developers can make new wallets, use existing wallets, sign transactions, and securely manage private keys.
- Accessing Blockchain Data: RPC (Remote Procedure Call) helps developers in accessing data from a blockchain network. These include confirming account balances, checking transaction history, reading contract information, and retrieving block data. This is required to build apps that run on the blockchain.
- Processing Transactions: Developers use RPC in sending transactions onto the blockchain. These include activities such as transferring cryptocurrencies, calling smart contract functions, or interacting with decentralized applications (dApps).
- Publishing Smart Contracts: Programmers can deploy and upload smart contracts to the blockchain with RPC. They provide the contract’s code and configurations required to deploy them correctly.
- Use of Smart Contracts: Through an RPC, developers can also interact with smart contracts in a network. They can call specific functions, change values stored in them, or read data that is being stored by the contract.